Wound Care
Use of PRP for wound care
Non-healing ulcers are a significant health problem worldwide and greatly impact one’s personal, professional, and social well-being.
Chronic or non-healing ulcers are wounds that fail to heal completely within the expected time, despite appropriate care. Such wounds are mainly present on the legs and can lead to conditions that require the amputation of lower limbs. This impacts a patient’s productivity and quality of life and adds an enormous financial burden.1
Non-healing ulcers are prevalent in 1.9%-13.1% of people globally. It is estimated that about 6.5 million U.S. patients are affected by chronic cutaneous non-healing wounds annually and about 10% of the world’s population is expected to develop chronic wounds at least once in their lifetime.2
Besides curing acute injuries, PRP interventions have also been effective in healing chronic ulcers (especially non-healing ones). 5 The procedure is considered safe and effective in treating chronic venous leg ulcers.6 PRP injections have
Below are the most common types of chronic or non-healing ulcers3
- Diabetic
- Venous
- Arterial
- Pressure
- Traumatic

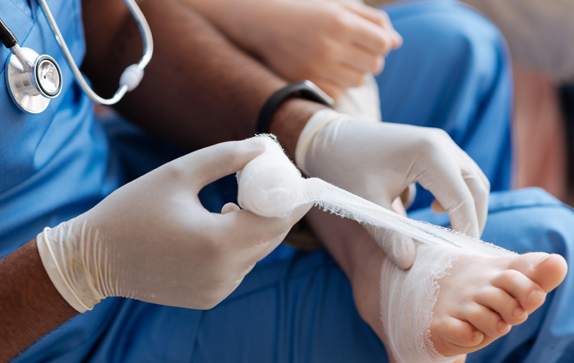
Treatment
Despite the efforts of doctors and other professional caregivers, many chronic ulcers fail to heal completely or stay unhealed for months or years. The ulcers may also recur after healing.
Autologous Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy
The use of autologous platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has been effective in the treatment of non-healing ulcers for more than 20 years. PRP consists of thrombocytes, cytokines, and various growth factors (proteins), which are secreted by α-granules of platelets. The components of PRP accelerate the natural healing process.
PRP is prepared from an individual’s blood (autologous) through centrifugation (a process to separate blood constituents). The concentration of platelets in PRP is two to six times higher than in blood.4
Besides curing acute injuries, PRP interventions have also been effective in healing chronic ulcers (especially non-healing ones).5 The procedure is considered safe and effective in treating chronic venous leg ulcers.6 PRP injections have positively impacted the lives of many diabetics because these injections can improve foot ulcer healing without any evident adverse side effects.7 PRP Concepts is leveraging its CASCADE Autologous Platelet System to yield a platelet-rich fibrin matrix, or PRFM (the clotted version of PRP), which can be more easily handled and manipulated than PRP when applying it onto the wound for treatment.
The PRFM treatment remains on the wound for several days to continuously deliver various growth factors in a coordinated fashion in order to improve wound healing.
THERE ARE NUMEROUS BENEFITS FROM USING AUTOLOGOUS PLATELET-RICH PLASMA:4
- Easy to use
- Cost-effective
- Reduces time taken for wound closure
- Decreases the area and depth of the wound
- Safe for patients, with negligible side effects
Patients with non-healing ulcers are strongly encouraged to consult a doctor. The doctor will evaluate whether they are candidates for the PRP therapy and proceed accordingly.

Sources:
- Xia, YiJun M.D.; Zhao, Jun M.D.; Xie, Juan M.D.; Lv, Yang M.D.; Cao, Dong Sheng M.D. The Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Dressing for Chronic Nonhealing Ulcers: A Meta-Analysis of 15 Randomized Controlled Trials, Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery: December 2019 – Volume 144 – Issue 6 – p 1463-1474.
- Greer, N., Foman, N. A., MacDonald, R., Dorrian, J., Fitzgerald, P., Rutks, I., & Wilt, T. J. (2013). Advanced Wound Care Therapies for Nonhealing Diabetic, Venous, and Arterial Ulcers. Annals of Internal Medicine, 159(8), 532.
- Suthar, M., Gupta, S., Bukhari, S. et al. Treatment of chronic non-healing ulcers using autologous platelet rich plasma: a case series. J Biomed Sci24, 16 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-017-0324-1
- https://www.ahrq.gov/sites/default/files/wysiwyg/research/findings/ta/prp/prp-wound-care.pdf
- Carter MJ, Fylling CP, Parnell LK. Use of platelet rich plasma gel on wound healing: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eplasty. 2011;11:e38. Epub 2011 Sep 15.
- Sarvajnamurthy S, Suryanarayan S, Budamakuntala L, Suresh DH. Autologous platelet rich plasma in chronic venous ulcers: study of 17 cases. J Cutan Aesthet Surg. 2013 Apr;6(2):97-9. doi: 10.4103/0974-2077.112671.
- Hu Z, Qu S, Zhang J, Cao X, Wang P, Huang S, Shi F, Dong Y, Wu J, Tang B, Zhu J. Efficacy and Safety of Platelet-Rich Plasma for Patients with Diabetic Ulcers: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2019 Jul 1;8(7):298-308. doi: 10.1089/wound. 2018.0842.
